Question
What are the functions of white blood cells?
Answers (1)
by Qcrew 15 years ago
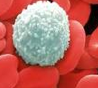
White blood cells are very important in terms of fighting viruses or bacteria. They can ingest disease-causing microorganisms, i.e. pathogens, and produce antibodies to destroy them.
White cells can also produce antitoxins that neutralise the toxins released by bacteria.
Although pathogens are living microorganisms, antibodies or antitoxins produced by white blood cells are not living things but specialised proteins.
Related Questions